In order to exist “in harmony with nature”, Bridgestone has continued to make comprehensive efforts to develop and utilize technologies that “value natural resources,” while addressing the urgent matter of global warming through efforts to “reduce CO2 emissions” based on the Environmental Mission Statement over many years. In becoming “nature positive”*, Bridgestone believes that a comprehensive approach and transformation that combines actions in various areas, such as efficient use of resources, sustainable production, and climate change countermeasures, as well as nature conservation, are necessary. Bridgestone will continue to evolve its Sustainability Business Model by incorporating the Science -Based Targets (SBTs) for Nature framework of “Avoid,” “Reduce,” “Restore and Regenerate,” and “Transform”.
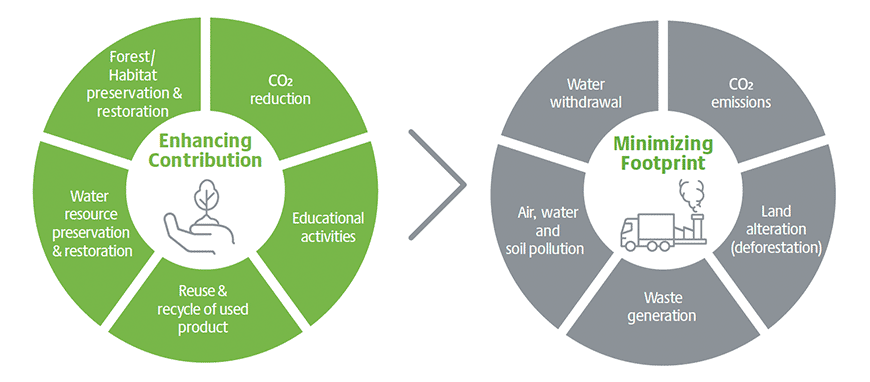
Bridgestone will strive into minimize the footprint of its business activities by reducing water withdrawal in water stress areas and emissions into the air and water. In parallel, it will enhance its contribution through conservation and restoration of ecosystems based on the long-term environmental vision of being “in balance with nature (Contribution > Footprint)” for 2050 and beyond, thereby contributing to realization of the vision of “living in harmony with nature” of the Convention on Biological Diversity.
* “Nature positive” means halting and reversing the loss of biodiversity and natural capital in order to put nature on the path to recovery. The intent behind this is to reduce the impact of business activities on biodiversity and natural capital, maintain and restore nature’s bounty, and transform socio-economic activities for the sustainable use of the natural capital.
Actions to achieve In Harmony with Nature
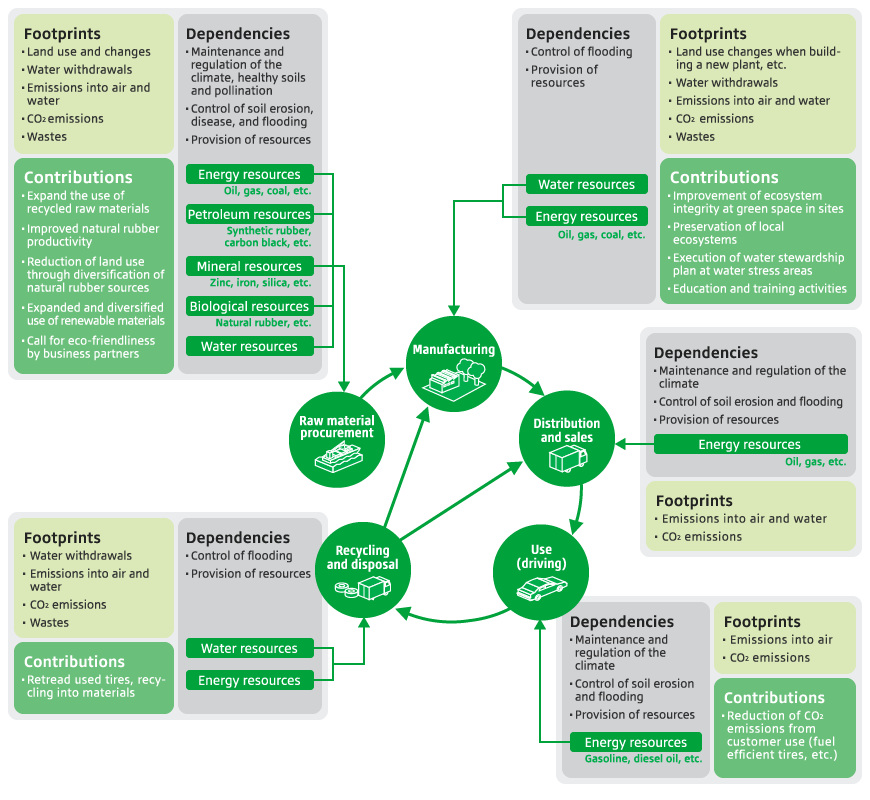
Bridgestone identifies and engages in activities related to its impact on and contribution to preservation/conservation of the environment throughout its product lifecycles and value chain.
- Minimizing footprint
(Examples)
・Reduce CO2 emissions in operations
・Reduce water withdrawal impact in water stress areas
・Reduce waste generated and amounts sent to landfills
・Request suppliers to consider biodiversity
・Strengthen environmental management to pollution prevention - Enhancing contribution
(Examples)
・Develop and expand solutions business to contribute to CO2 reduction
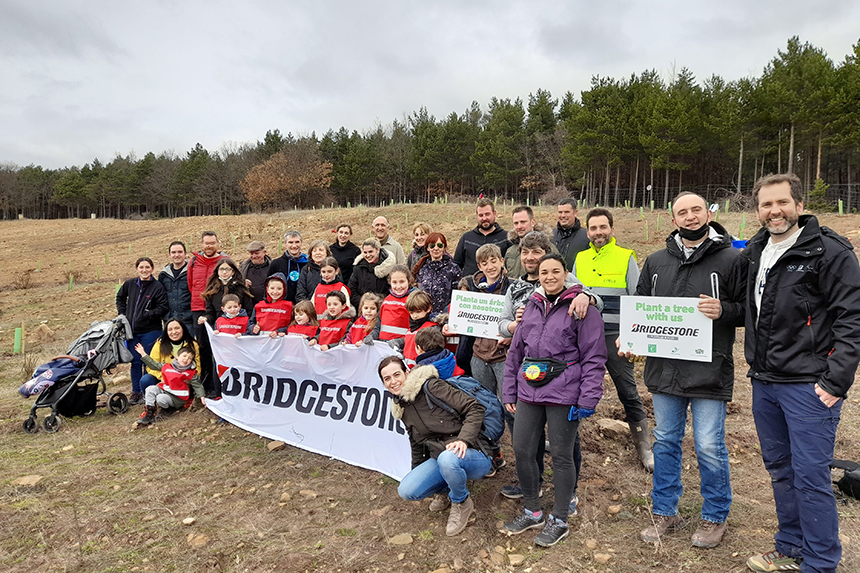
・Preserve and restore ecosystems around Bridgestone facilities
・Conduct water conservation activities within communities
・Contribute to enhancement of the circular economy
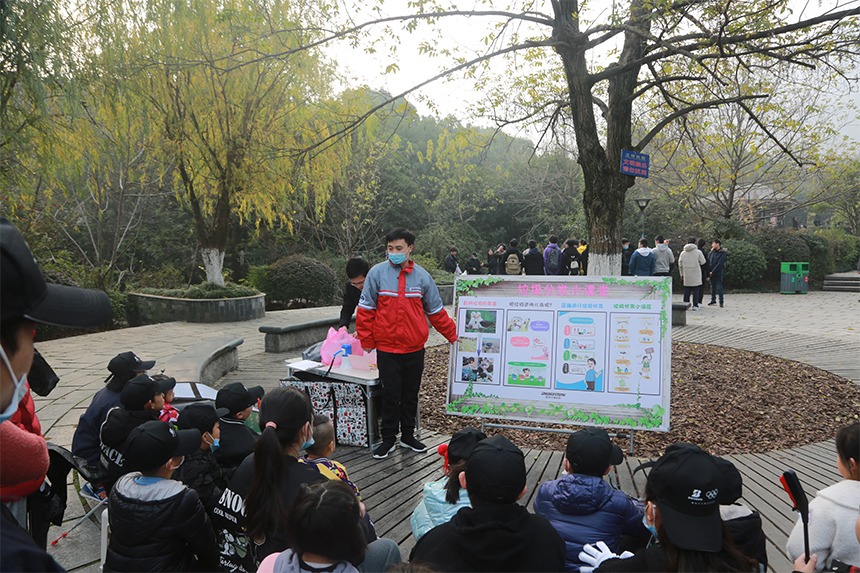
・Introduce biodiversity educational program