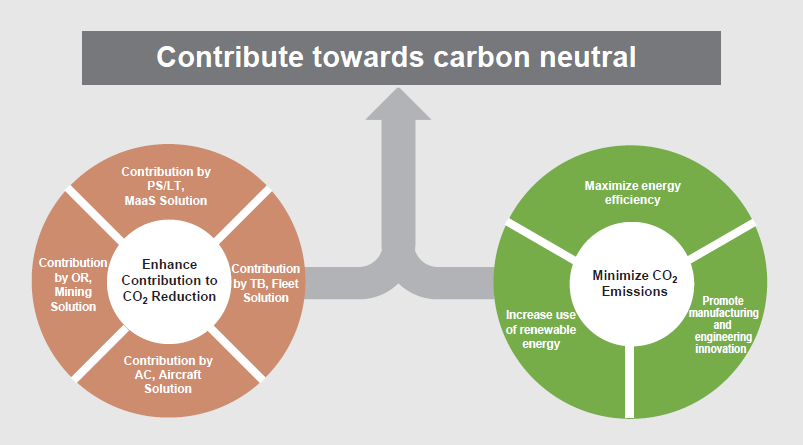
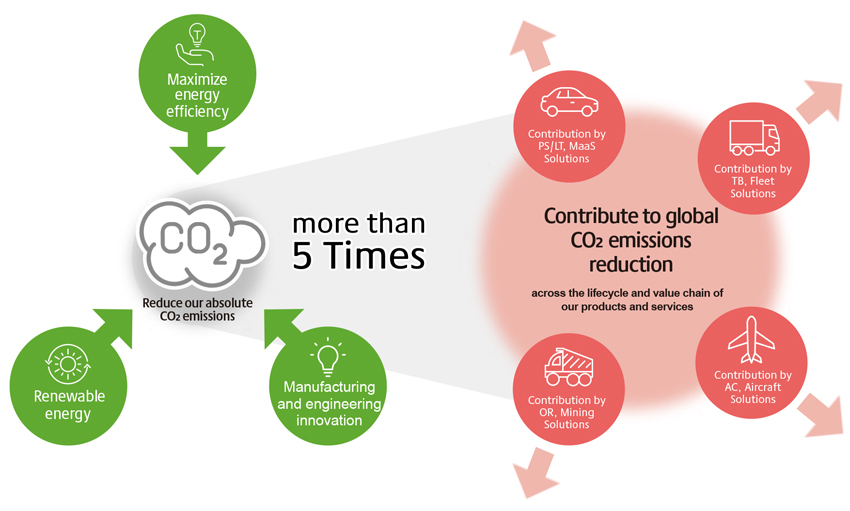
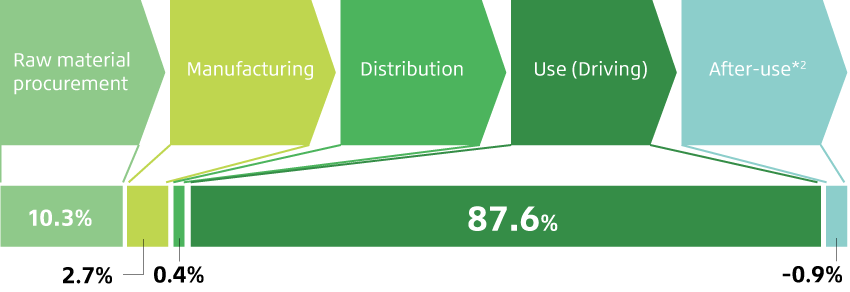
Bridgestone is promoting co-creation with stakeholders by encouraging open innovation in technology, business models, and design, and combining technologies in various fields. In terms of climate change action, Bridgestone is also working with other organizations and businesses to accelerate carbon neutral initiatives. In Japan, it is working as a member of the Japan Climate Initiative (JCI) and the Tokyo Zero-emission Innovation Bay council. In April 2021, Bridgestone endorsed a message by JCI calling for the government of Japan to set ambitious greenhouse gas emission reduction targets to realize the goals of the Paris Agreement. The message, which calls for a 2030 reduction target of "going beyond 45% - aiming for a 50% emission reduction," was delivered as an open letter to Japan’s Prime Minister, Foreign Minister, Minister of Economy, Trade and Industry, and Minister of the Environment, and published by various media outlets.
In 2023, Bridgestone participated in the review of the Revised Act on the Rational Use of Energy, a law related to action against climate change, by submitting an opinion to promote the proper evaluation of electrification technology that contributes to the reduction of CO2 emissions with electricity from renewable energy sources. It also supports the Japanese government’s actions to mitigate climate change aligned with the Paris Agreement by enhancing its initiative towards carbon neutrality as well as complying to the laws related with climate change.
Moreover, Bridgestone is a major member of the Japan Rubber Manufacturers Association, which has been working to achieve 2030 mid-term targets to reduce CO2 emissions during manufacturing as part of the Japanese Business Federation’s Commitment to a Low Carbon Society, which plays a central role in the industrial sector’s commitment. In Japan, Bridgestone is also participating in the Port of Kitakyushu Carbon Neutral (CNP) Study Group, which is comprised of companies, the national government, and the City of Kitakyushu. The study group was established by the Kyushu Regional Development Bureau of the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism and the City of Kitakyushu with the aim of reducing overall greenhouse gas emissions to zero at the Port of Kitakyushu, a node for international logistics and an industrial hub. In 2022, this study developed the Port of Kitakyushu CNP Formation Plan (Draft).
Furthermore, Bridgestone has pledged its support for the Challenge Zero initiative launched by the Japan Business Federation in collaboration with the Japanese government, which aims to realize a decarbonized society for Japan as a long-term goal in line with the international framework of the Paris Agreement.
In 2024, Bridgestone joined the GX League in Japan, a forum for cooperation between a group of companies and the government, universities, and academic institutions to meet greenhouse gas reduction targets and increase industrial competitiveness, by using Japan’s goal of carbon neutrality by 2050 as an opportunity for economic growth. Bridgestone will collaborate with members of the forum to advance initiatives aimed at transforming economic and social systems.
In participating in or reviewing climate change-related initiatives and organizations, Bridgestone periodically evaluates these initiatives and organizations based on their affinity with its business strategy direction, including its goals toward carbon neutrality. If there is a large discrepancy, Bridgestone will reconsider its relationship with them.