Bridgestone faces various cybersecurity risks, including new, emerging, and significantly heightened threats. These risks are evaluated across multiple categories, such as data protection, threat and vulnerability management, and security governance. Long-term and externally influenced risks include economic instability and escalating geopolitical tensions between countries where Bridgestone operates. These conditions could lead to actions and attacks by state-sponsored threat actors, activist hacker groups, or other malicious actors. Due to its operations spanning over 150 countries, the vast range of products it offers, and its large threat landscape, Bridgestone is exposed to a wide range of cybersecurity risks, influenced by the varying cultural and regulatory environments of different regions. Furthermore, due to the significant risks of privacy and personal data breaches, which could undermine customer trust, Bridgestone considers protecting customers' personal information a critical responsibility across its entire business, including the tire, solutions, and diversified products segments.
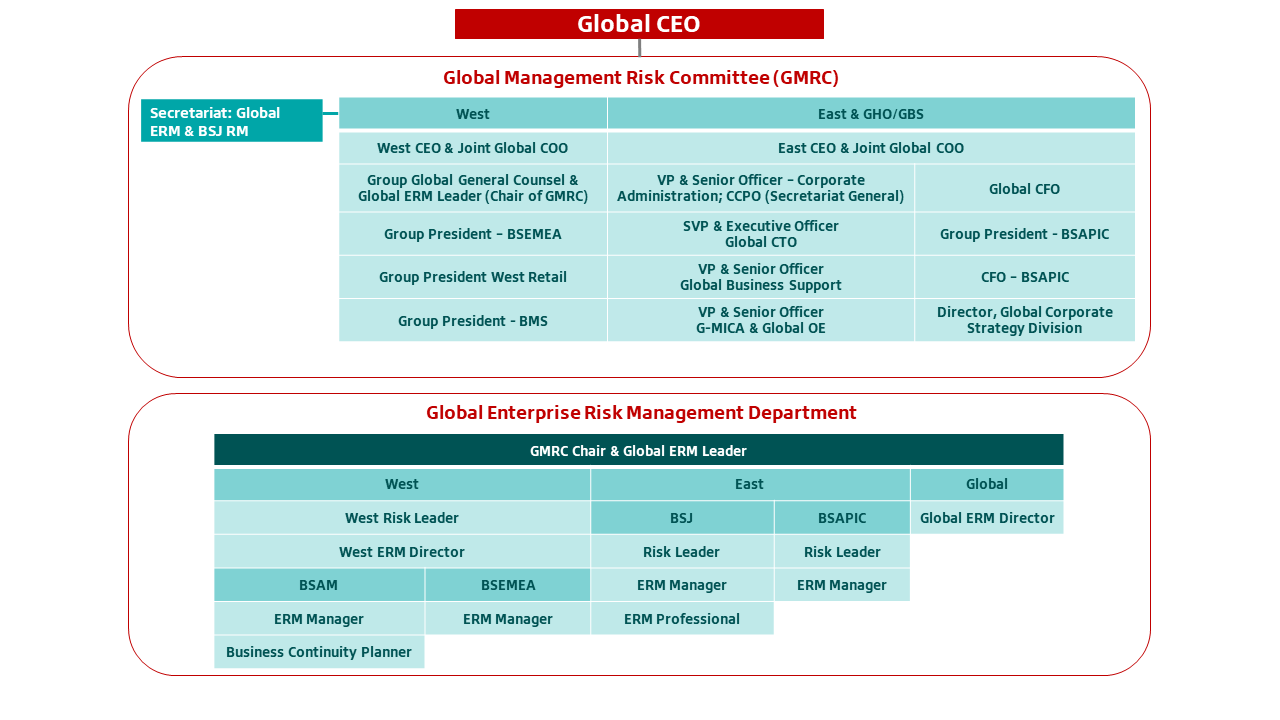
Bridgestone has created a global Information Security department led by a global Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) to secure the enterprise while supporting agile and resilient operations. The global Information Security department takes a wide range of measures to maintain and strengthen the Company’s global information security program, including but not limited to the following:
- Implementing global information security policies and controls based on the ISO/IEC 27001 information security controls.
- Enhancing awareness of information security among employees through e-learning programs and phishing awareness campaigns.
- Protecting data with technical cybersecurity measures such as encryption, data access restrictions, and threat detection monitoring.
Bridgestone has established this global organizational structure to quickly respond to information security incidents and regularly conducts both internal and external audits to verify the effectiveness of security controls. Additionally, Bridgestone continues to strengthen measures to provide effective monitoring of its websites, networks, and other systems, as well as the improvement of security controls such as email filtering to help detect of suspicious emails.
In 2020, Bridgestone conducted an initial assessment of its IT digital maturity to identify long-term cybersecurity risk, and the global Information Security department continues to mature cyber risk assessment and response activities. Additionally, in 2022, a Global Cyber Risk Working Group was created, led by the global Information Security leader. The Working Group is composed of senior IT executives and employees, as well as other ancillary departments and functions, to serve as a cross-functional team to address cyber resiliency and globally align strategy and the execution of IT programs and systems.
In Japan, Bridgestone Corporation and its Group companies take a systematic approach to IT security under the direction of the Chief Information Officer to prevent IT security incidents, including leaks of customer data and other confidential information. The Company formulates corporate standards and rules on IT security, which are reviewed and revised to stay abreast of technological advancements and changes in IT risks. It sets particularly strict standards for information systems that handle personal information.
Bridgestone sells products in more than 150 countries worldwide, and the potential of a data security incident or ransomware attack which may impact its business operations could vary considerably from region to region based on local laws and regulations. The impact of a data security incident could lead to significant operational disruption and/or result in fines and penalties or damages under various privacy and data security laws, rules, regulations, or lawsuits brought by impacted individuals. A data security incident might also damage the Bridgestone brand now and in the future. Based on the complexity of cybersecurity threats, Bridgestone reviews multiple information and communication security categories when evaluating emerging cyber risks, including topics such as data protection, threat and vulnerability management, identity and access management, and security governance.
As stated earlier, Bridgestone has created a global Information Security department under the direction of a global Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) to counter targeted attacks and other advanced cyber threats. The global Information Security department takes measures to maintain and continually improve upon a global information security program through the incorporation of global information security policies and controls, as well as to enhance the awareness of information security among employees through e-learning programs.
The Bridgestone Code of Conduct contains a specific section on privacy and personal data. Furthermore, to comply with data protection laws and regulations, certain SBUs have appointed a designated data protection lead (if required by law) or privacy officer and continue to implement and maintain robust privacy programs and associated policies. They have further developed methods to monitor and comply with the emerging privacy laws being adopted by an increasing number of governments in their territories.
The privacy professionals in the various Bridgestone Group companies have focused on compliance with the privacy laws such as Europe’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and other privacy laws in the EMEA region, Brazil’s Lei Geral de Proteção de Dados (LGPD) and other privacy laws in Latin America, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and the 18 other U.S. state privacy laws that have been passed as of February 2025, as well various data protection acts in the APIC region.
Bridgestone and its Group companies in Japan believe that protecting personal information is an important employee responsibility. Bridgestone in Japan has formulated a Privacy Policy that reflects these principles. Based on this policy, the Company conducts ongoing training for all its employees and its Group companies’ employees in Japan and maintains a well-defined structure for information management.
For the privacy policy, also please see: Privacy Policy | Bridgestone