Bridgestone’s environmental mission is “to help ensure a healthy environment for current and future generations....” The environmental mission includes three focal points: existing in harmony with nature, valuing natural resources, and reducing CO2 emissions. The mission’s “In harmony with nature” refers to biodiversity conservation and the Bridgestone Group’s efforts to minimize the impact of operations on the overall ecosystem.
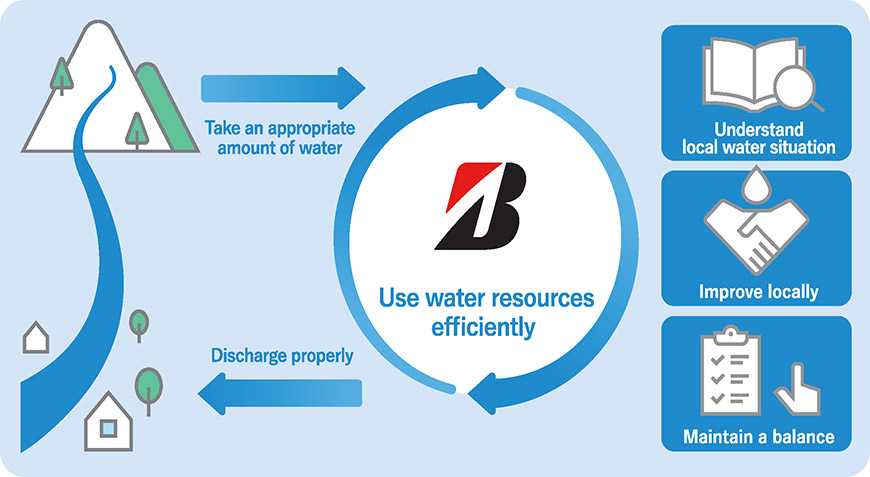
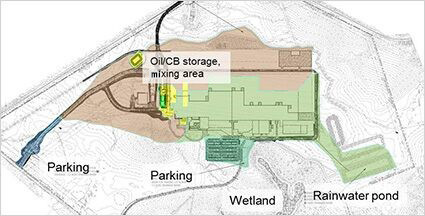
The Group is engaged in various activities to help minimize the impact of its business activities on wildlife and natural habitats, while also engaging in numerous activities to help improve the ecology at the production sites and the communities it calls home. These include reducing emissions, conserving water and other important natural resources, and implementing ecological improvement and education-related projects at business locations and in local communities.
The Group intends to be even more ambitious in its activities in response to the continued importance of social and environmental issues, and the potential impact on the environment caused by its business growth. Building on the various initiatives introduced in the previous mid-term target to reduce environmental impact on an ongoing basis, the Group is working to improve on these achievements and minimize its footprint even more.